What Does Carbohydrate Mean In Biology
Carbohydrates contain carbon hydrogen and oxygen in a fixed ratio. Aldoses bear terminal aldehyde or CHO group eg glyceraldehyde xylose ribose glucose galactose while ketoses have an internal ketone or CO group eg dihydroxy acetone erythrulose ribulose xylulose fructose sedoheptulose.

Examples Of Carbohydrates Biology Dictionary
A carbohydrate is either a sugar or a polymer of sugars.

What does carbohydrate mean in biology. A carbohydrate is an organic compound such as sugar or starch and is used to store energy. Carbohydrates are covalently bound to either protein or lipid to form glycoproteins or glycolipids. Independent variable duct lead.
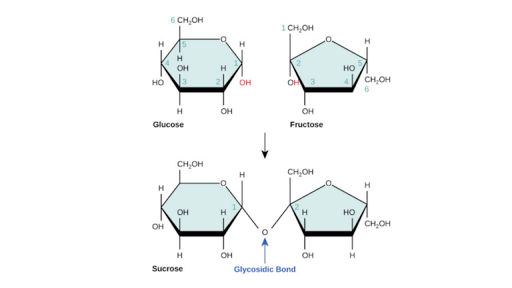
During this condensation reaction a hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide combines with another hydrogen atom forming and releasing a water molecule Figure 2. For every one carbon atom a carbohydrate contains one oxygen atom and two hydrogen. Relatively complex carbohydrate s are known as polysaccharides.
The n represents the number of times the basic CH 2 O unit is repeated eg. Carbohydrate s literally hydrates of carbon are chemical compound s that act as the primary biologic al means of storing or consuming energy other forms being fat and protein. In the case of carbohydrates the small repeating units are called monosaccharides.
Deductive reasoning in- not. Carbohydrates serve as energy sources and as essential structural components in organisms. Sugar is an example of a carbohydrate.
In chemistry a compound is a pure substance of two or more elements stuck together. Carbohydrates are broken down by the body into glucose which can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Roots Prefixes and Suffixes in Biology Unit 1.
Carbohydrates are formed by green plants from carbon dioxide and water during the process of photosynthesis. A disaccharide is any carbohydrate made up of two monosaccharides that are joined covalently by an O-glyosidic bond. Most carbohydrates have twice as much hydrogen as oxygen and carbon.
Carbohydrates are an example of the many types of organic compounds. A polymer is two or more simple sugars joined together. Carbohydrate s are naturally produced by plant s.
They fuel the processes in your body. In addition part of the structure of nucleic acids which contain genetic information consists of. The formula of a carbohydrate is always CH 2 O n.
This is the formula shared by glucose and other simple sugars like fructose. Like most organic compounds carbohydrates are built of small repeating units that form bonds with each other to make a larger molecule. Study of Biology RootPrefixSuffix Meaning Examples a- not without.
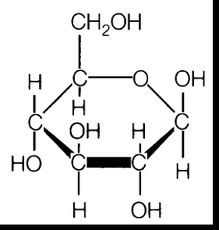
A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Carbohydrates are polyhydroxy aldoses ketoses and their condensation products. Its four major element constituents are carbon hydrogen oxygen and nitrogen.
Abiotic bio- life living. Any of various neutral compounds of carbon hydrogen and oxygen as sugars starches and celluloses most of which are formed by green plants and which constitute a major class of animal foods. Biology de- away from down.
Carbohydrates can also be defined chemically as neutral compounds of carbon hydrogen and oxygen. Common disaccharides include lactose maltose and sucrose. Where n 6 the molecular formula is C 6 H 12 O 6.
All carbohydrates are formed from the elements carbon C hydrogen H and oxygen O. Carbohydrates are known as one of the basic components of food including sugars starch and fibre which are abundantly found in grains fruits and milk products. Carbohydrates come in simple forms such as sugars and in complex forms such as starches and fiber.
An organic compound is a compound that in general contains carbon covalently bound to other atoms especially Carbon-Carbon C-C and Carbon-Hydrogen C-H. A simple sugar is known as a monosaccharide. Carbohydrates are an important source of energy.
The body breaks down most sugars and starches into glucose a simple sugar that the body can use to feed its cells. The definition of a carbohydrate is an organic compound that occurs in living tissues or food and that can be broken down into energy by people or animals. A carbohydrate is an organic compound that is made of hydrogen carbon and oxygen.
Inductive reasoning Unit 2. Glycoproteins act as a hormone Thyroid-stimulating hormone TSH and erythropoietin enzyme Phosphatase lipase pepsinogen receptor integral membrane protein mucins and Cadherin is the major adhesion molecule. In food science carbohydrate means any food rich in starch such as cereals bread and pasta.
Medical Definition of carbohydrate. Carbohydrates are carbon based molecules with hydrogen and oxygen bonded to a chain of carbon atoms. Carbohydrates are organic compounds.
An organic compound is a compound that contains hydrogen and carbon hydrocarbons. Biodiversity -ology study of. The main function of carbohydrates is to provide energy and food to the body and to the nervous system.

Carbohydrates Definition Classification With Structure And Functions

Carbohydrates Biological Molecules Simplified 1 Youtube

Examples Of Carbohydrates Biology Dictionary
Carbohydrates Article Chemistry Of Life Khan Academy
Carbohydrates Biology Encyclopedia Plant Body Process Animal Structure Water Molecules Energy

Carbohydrates Biomolecules Learnbiology Net

Aqa Subject Content Biological Molecules Carbohydrates
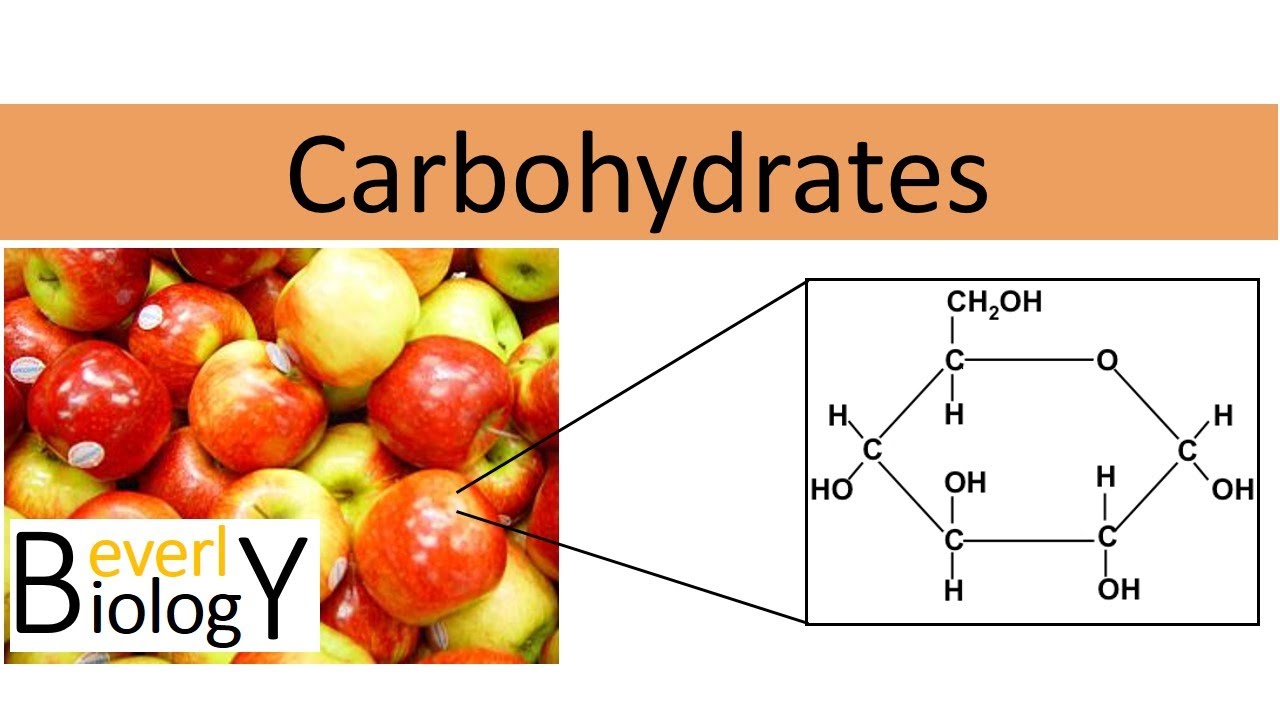
Carbohydrates Regular Biology Youtube
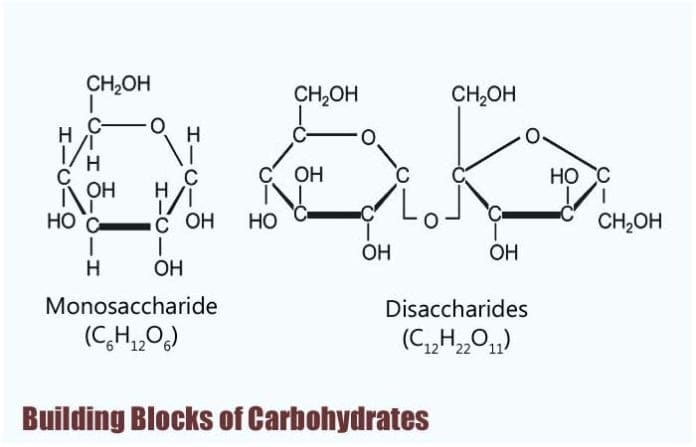
Building Blocks Of Carbohydrates Types Properties Functions
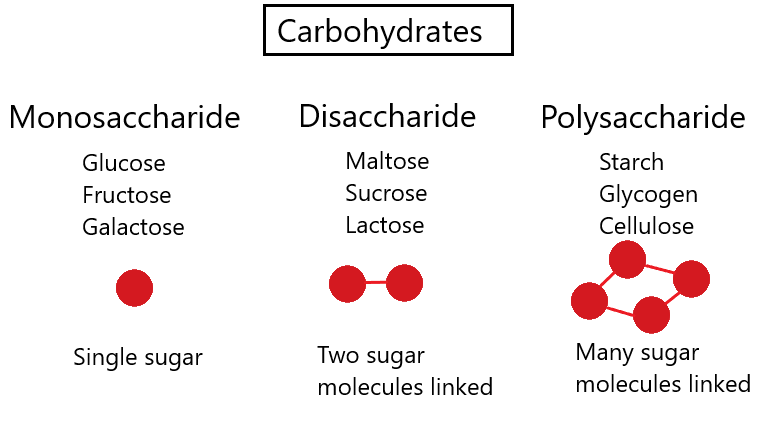
Biological Molecules Igcse Biology Notes 2020

Carbohydrate Structure Formula Types What Are Carbohydrates Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Carbohydrates Definition Classification With Structure And Functions
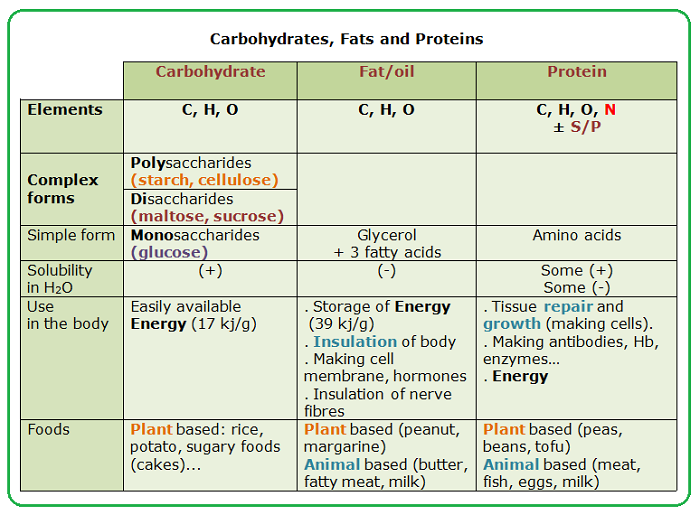
Main Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats And Proteins Biology Notes For Igcse 2014

Carbohydrate Biological Significance Britannica
1 10 Carbohydrates Biology Libretexts
Biological Macromolecules Carbohydrates Schoolworkhelper

Introduction To Carbohydrates Video Khan Academy
Posting Komentar untuk "What Does Carbohydrate Mean In Biology"